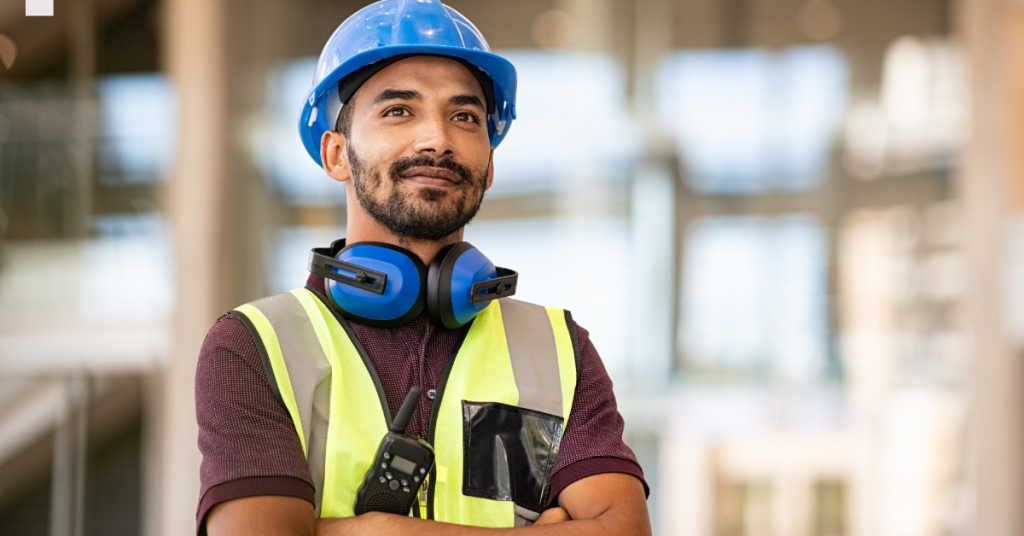
Noise is an unavoidable part of many work environments—from construction zones and factories to airports and landscaping sites. While these sounds may seem like a normal part of the job, prolonged exposure can lead to a serious and often irreversible condition: noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). According to the CDC, around 22 million workers in the United States are exposed to hazardous noise levels at work each year. Unfortunately, many of them don’t realize the damage until it’s too late.
That’s where hearing protection comes in. Much like hard hats and safety goggles, ear protection is essential personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to shield your hearing from excessive noise. But with so many options on the market—ranging from foam earplugs to high-tech electronic earmuffs—choosing the right protection for your specific jobsite can feel overwhelming.
This article is here to help. We’ll walk you through why hearing protection is so important, the types available, and how to choose the best solution for your needs. Whether you work in heavy construction, operate loud machinery, or spend hours in a noisy warehouse, there’s a hearing protection option tailored for you. Let’s dive into the top picks and best practices for protecting your ears on the job.
Why Hearing Protection at Work Matters
Hearing loss isn’t just an inconvenience—it’s a serious health issue that can affect communication, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. For workers in noisy environments, the threat of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is ever-present. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets legal limits on noise exposure in the workplace, typically capping it at 90 decibels (dBA) over an 8-hour shift. But many job sites routinely exceed that threshold, exposing workers to sounds that can gradually—and permanently—damage their hearing.
The real danger lies in how quietly this damage happens. NIHL typically develops over time, without pain or obvious symptoms. By the time a worker notices their hearing has declined, the loss is often irreversible. Common early signs include difficulty understanding speech, needing to turn up the volume on devices, or a persistent ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
Chronic exposure to high noise levels doesn’t just damage hearing—it also contributes to other workplace risks. Studies have shown that excessive noise can impair concentration, reduce job performance, and even increase the risk of accidents due to misheard warnings or instructions. This makes hearing protection a safety issue not just for the individual, but for the entire team.
Moreover, hearing loss can have emotional and social consequences. Workers who experience NIHL often report feelings of isolation, frustration, and depression. These effects can linger long after the workday ends, affecting family life, social interactions, and mental health.
Fortunately, hearing loss from workplace noise is 100% preventable. The key is consistent and proper use of high-quality hearing protection. Whether you’re using simple foam earplugs or advanced electronic earmuffs, wearing the right protection every time you’re in a noisy environment is crucial. Employers also play a vital role by conducting regular noise assessments, providing appropriate hearing protectors, and offering training on their use.
In short, protecting your ears at work isn’t optional—it’s essential. Understanding the risks and making hearing safety a daily habit can make the difference between healthy hearing for life and a future filled with silence or ringing.
Types of Hearing Protection Devices (HPDs)
When it comes to shielding your ears from hazardous noise levels at work, not all hearing protection is created equal. Different jobs and environments call for different types of hearing protection devices (HPDs), each with unique features, benefits, and levels of comfort. Understanding your options is the first step in choosing the most effective solution for your work setting.
Earplugs
Earplugs are small devices inserted directly into the ear canal to block noise. They are often made from foam, silicone, or rubber and come in both disposable and reusable varieties. Foam earplugs are a popular choice due to their affordability and high noise reduction ratings (NRR), often ranging from 20 to 33 dB.
Silicone or pre-molded earplugs are more durable and may offer a custom fit. Some high-end models are molded specifically to the user’s ear for maximum comfort and protection. Earplugs are lightweight and convenient, making them ideal for long-term wear and high-temperature environments. However, they must be inserted correctly to work effectively, and hygiene can be a concern if they are reused without proper cleaning.
Earmuffs
Earmuffs consist of cushioned ear cups connected by a headband that fits over the top of the head. They cover the entire ear and work by sealing out noise. Earmuffs are generally easier to put on and take off than earplugs, making them a good option for intermittent noise exposure or when multiple users share the same device.
While they usually provide slightly lower NRRs than earplugs (typically 15–30 dB), earmuffs offer more consistent protection since they don’t rely on proper insertion. They are also more durable and can be used in combination with earplugs for environments with extreme noise levels. However, earmuffs can be bulky and may become uncomfortable in hot or confined spaces.
Canal Caps
Canal caps are a hybrid solution featuring earplug-like tips attached to a flexible band. The tips rest at the entrance of the ear canal rather than inside it. These are convenient for jobs where workers need to frequently insert and remove hearing protection, as they can hang around the neck when not in use.
While not as protective as fully inserted earplugs or sealed earmuffs, canal caps provide a good balance of protection and ease of use. They’re best suited for moderate noise levels and short-term exposure.
Custom Molded Protection
For workers who need long-term, high-performance hearing protection, custom molded earplugs or in-ear monitors can offer the best fit and comfort. These are made from impressions of the user’s ears and provide a personalized seal against noise. Though more expensive, they offer consistent protection, reduce pressure points, and can last for years with proper care.
Each type of HPD has its place depending on the specific work conditions, duration of use, and personal comfort. Knowing the options allows workers and employers to make informed choices that ensure both safety and usability.
Top Hearing Protection for Different Job Settings
Choosing the right hearing protection depends not just on the level of noise, but also on the nature of your work environment. The best device for a construction site may not be ideal for a factory, and what works in landscaping might be uncomfortable for long shifts in a warehouse. In this section, we’ll explore top hearing protection options tailored to various job settings, taking into account comfort, effectiveness, durability, and user needs.
Construction Sites
Recommended Protection: Over-ear earmuffs with high NRR (Noise Reduction Rating), such as the 3M Peltor X5A or Howard Leight by Honeywell Impact Pro.
Construction zones often feature a mix of continuous and impulse noise—from jackhammers and saws to heavy machinery and hammering. Earmuffs offer robust protection and are easy to slip on and off when moving between high and low-noise areas. Look for models with foam padding, wide ear cups, and adjustable headbands for all-day comfort. For extremely noisy tasks, consider doubling up with earplugs under earmuffs.
Factories and Industrial Settings
Recommended Protection: Reusable earplugs like Etymotic ER20XS or Moldex Rockets, or canal caps for intermittent exposure.
Factory workers often experience long shifts around loud, consistent noise, like conveyor belts, stamping machines, or compressors. Earplugs are discreet, lightweight, and effective, especially in hot or enclosed spaces where earmuffs might feel too bulky. Choose a reusable option to reduce waste and ensure consistent performance over time.
Landscaping and Outdoor Work
Recommended Protection: Electronic earmuffs such as the Walker’s Razor Slim Electronic Muff or Peltor Sport Tactical 500.
Outdoor workers need protection from noise produced by lawnmowers, chainsaws, and blowers, but they also need to hear environmental cues like approaching vehicles or team communications. Electronic earmuffs use built-in microphones to amplify ambient sounds while blocking loud noises above safe thresholds. They’re a top choice for those who want safety without losing situational awareness.
Airports and Aviation
Recommended Protection: Dual protection—earplugs and earmuffs together.
Airport ground crews and maintenance staff are exposed to one of the loudest work environments, with noise levels from jet engines often exceeding 140 dB. OSHA recommends double protection in such cases. Combine high-NRR foam earplugs with professional-grade earmuffs to achieve the highest level of defense. Brands like David Clark and 3M Peltor Aviation series offer durable options specifically for aviation use.
Warehouses and Office Settings with Intermittent Noise
Recommended Protection: Canal caps or electronic earplugs such as the Eargasm High Fidelity Earplugs.
For environments where noise is occasional—like alarms, forklift beeping, or short bursts of machinery—lightweight and easy-to-remove protection is ideal. Canal caps rest outside the ear canal and can be quickly inserted when needed. Electronic earplugs provide adaptive protection, blocking loud sounds while allowing speech and ambient noise through.
Each workplace presents its own set of challenges, and the right hearing protection balances effectiveness with usability. Comfort, convenience, and communication are just as important as decibel reduction, especially for all-day wear. Selecting the best gear for your jobsite ensures not only compliance with safety regulations but also long-term hearing health.
Electronic vs. Passive Hearing Protection
When choosing hearing protection for work, one major decision is whether to go with electronic (active) or passive devices. Both types aim to reduce noise exposure, but they work in different ways and offer distinct advantages depending on the jobsite, noise type, and user needs.
Passive Hearing Protection
Passive devices block sound using physical barriers—usually foam, plastic, or a combination of materials—to muffle noise. This includes standard foam earplugs, pre-molded plugs, and traditional earmuffs. They’re simple, affordable, and effective, especially for continuous, high-decibel environments.
Pros of Passive Protection:
- No batteries or electronics to manage
- Budget-friendly and widely available
- High NRR options, especially when doubling earplugs and earmuffs
- Reliable performance with minimal maintenance
Cons:
- May block all sound, including speech and warning signals
- Can feel isolating or uncomfortable in long-term use
- Fit and seal are critical—improper use reduces effectiveness
Passive protection works best in environments with constant, predictable noise—like factories, metal shops, and construction sites where communication is minimal or conducted by hand signals.
Electronic Hearing Protection
Electronic or “active” protection uses built-in microphones and speakers to differentiate between safe and harmful sounds. These devices amplify low-level sounds like conversation or ambient noise while instantly suppressing loud, dangerous noise above 85 dB. They’re most commonly found in earmuffs but are also available in in-ear formats.
Pros of Electronic Protection:
- Situational awareness—you can still hear voices, alarms, and environmental sounds
- Communication-friendly, ideal for teams or public-facing workers
- Often includes Bluetooth for device pairing (music, phone calls, radio)
- Some models have directional microphones for enhanced clarity
Cons:
- Higher cost than passive devices
- Requires batteries or charging
- Can be heavier or bulkier depending on the model
- May not provide as high a NRR as passive devices alone
Electronic protection is ideal for jobs where both hearing and communication are critical—such as construction foremen, airport workers, landscapers, and warehouse supervisors. They allow users to stay connected without sacrificing safety.
Some workers even combine the two—wearing foam earplugs under electronic earmuffs for dual protection with communication benefits. Your choice should consider the type of noise, how long you’re exposed, and whether you need to stay aware of your surroundings.
Ultimately, both electronic and passive devices have their place. The best protection is the one that fits your job, feels comfortable, and you’ll wear consistently.
Tips for Proper Use and Maintenance
Even the best hearing protection won’t do its job if it’s not used correctly. To maximize the effectiveness of your hearing protection devices (HPDs), proper use, maintenance, and replacement are essential. In this section, we’ll walk through best practices to ensure you’re getting the full benefit of your earplugs, earmuffs, or other protective gear—every day, on every jobsite.
Proper Fit Is Critical
The first step to effective hearing protection is ensuring a proper fit. A poorly fitted earplug or loose earmuff can significantly reduce the Noise Reduction Rating (NRR), leaving your ears vulnerable.
- Earplugs: Roll foam plugs into a tight cylinder before gently inserting them into the ear canal. Hold them in place for a few seconds to allow the foam to expand and seal properly. Improper insertion is one of the most common mistakes.
- Earmuffs: Ensure the ear cups fully enclose your ears and that the headband provides even pressure. Hair, hats, or safety glasses can break the seal, so adjust as needed to avoid gaps.
- Custom or Pre-Molded Devices: These should slide in comfortably and create a secure seal without pain or irritation.
Take the time to learn and teach others how to use HPDs properly—especially if your workplace relies on shared gear.
Keep Them Clean
Like any piece of safety equipment, HPDs need to be kept clean to work properly and avoid introducing dirt or bacteria into the ear canal.
- Foam earplugs: Disposable plugs should be thrown away after each use. Reusing them can lead to reduced performance and hygiene concerns.
- Reusable earplugs: Wash with mild soap and warm water, then air dry completely before storing.
- Earmuffs: Wipe down ear cushions and headbands regularly with disinfectant wipes or a damp cloth. Replace foam inserts or cushions when they show signs of wear.
Regular cleaning not only extends the life of the equipment but also ensures your ears stay healthy and free of irritation or infection.
Store Them Properly
Storing your HPDs correctly prevents damage and contamination. Use a dedicated storage case or a clean, dry compartment in your tool bag or locker. Avoid tossing them into pockets or letting them sit in dusty or oily environments.
Moisture, extreme temperatures, and crushing forces (like sitting on earmuffs) can degrade materials over time. Treat your hearing protection gear like the safety-critical tool it is.
Know When to Replace
HPDs don’t last forever. Look for signs of wear, damage, or loss of function:
- Foam earplugs no longer expand properly
- Earmuff cushions become hard, cracked, or lose their seal
- Headbands lose tension and no longer hold earmuffs snugly
- Electronic devices have inconsistent sound suppression or battery issues
Manufacturers often provide guidelines for replacement timelines—follow them to stay protected.
Use It Every Time
Consistency is key. One of the biggest risks is intermittent use—taking your ear protection off for “just a minute” around loud machinery. Even short bursts of intense noise can cause permanent damage. Make it a habit to wear hearing protection the moment you enter a noisy zone, and don’t remove it until you’re safely out.
Train and Communicate
If you’re an employer, provide proper training for all employees on how to choose, fit, wear, and maintain their HPDs. Encourage questions and provide replacements readily. A culture that values hearing safety starts with informed, empowered workers.
Conclusion
Hearing is one of our most vital senses—especially in the workplace, where awareness and communication can mean the difference between safety and danger. Yet too often, hearing protection is overlooked or improperly used, leaving workers vulnerable to irreversible noise-induced hearing loss. The good news? This kind of hearing damage is entirely preventable with the right tools and habits.
Whether you’re facing the thunder of a construction site, the steady hum of a factory floor, or the occasional roar of landscaping equipment, there’s a hearing protection solution designed to meet your needs. From affordable foam earplugs to high-tech electronic earmuffs, today’s options are more advanced, comfortable, and effective than ever. The key is choosing the device that fits your environment, understanding how to use it properly, and making it a non-negotiable part of your daily routine.
Employers play a critical role, too. Providing quality hearing protection, offering training, and creating a safety-first culture ensures that employees not only stay protected but also feel empowered to safeguard their long-term health.
Don’t wait for a warning sign like ringing ears or muffled hearing to start taking action. Think of hearing protection as a hard hat for your ears—essential, everyday gear that keeps you safe and sound for the long haul.
FAQ
What is the best hearing protection for extremely loud work environments?
For extremely loud environments (above 100 dB), the best option is dual protection—using earplugs and earmuffs together. This combination significantly increases noise reduction, often achieving an effective NRR of over 30 dB. Look for high-rated products like foam earplugs combined with heavy-duty earmuffs such as the 3M Peltor X5A or similar industrial-grade models.
Are electronic hearing protectors safe and effective for noisy jobsites?
Yes, electronic hearing protectors are both safe and effective. They offer the advantage of amplifying safe sounds like speech or warning signals while automatically suppressing loud, damaging noises. They’re ideal for workers who need situational awareness and communication while still staying protected. Just make sure they meet NRR standards for your specific environment.
How often should I replace my hearing protection gear?
Replacement depends on the type and usage:
Disposable foam earplugs: After each use
Reusable earplugs: Every few weeks to months, depending on wear and cleaning
Earmuffs: Every 6–12 months for cushions, sooner if cracked or stiff; headbands and internal components may last longer but should be replaced if damaged
Always inspect gear regularly and replace it if the fit, seal, or comfort is compromised.
Can I wear hearing protection all day at work?
Yes, and in many jobs, you should. Good hearing protection is designed to be worn for extended periods. Choose products that are comfortable, lightweight, and breathable. If discomfort arises, try a different style or fit. Rotating between different types (e.g., earplugs and earmuffs) can also help reduce fatigue.
Do I need hearing protection if I only encounter loud noise occasionally at work?
Even short-term exposure to loud noise can damage hearing permanently. If you’re around tools, machines, or activities that produce bursts of high noise—even just a few times a day—wearing hearing protection is essential. Canal caps or electronic devices that are easy to remove and reinsert are great for intermittent exposure.
“This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you are concerned about your hearing or ear health, please consult a qualified healthcare provider.”